AAAT
IMI与AIF联袂出品:本土化还是国际化?——2018 全球银行国际化报告
时间:2018年09月27日 作者:IMI
导读:
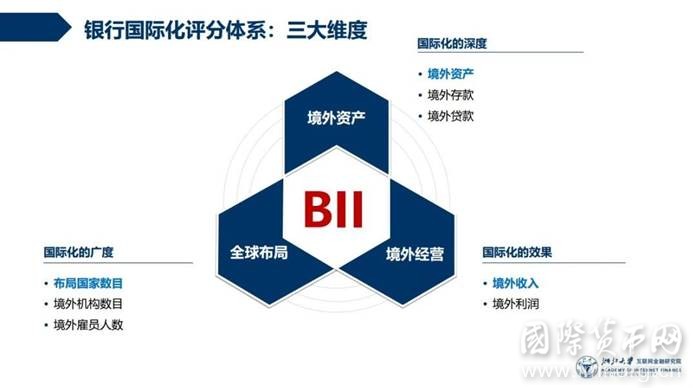 一、 最国际化银行
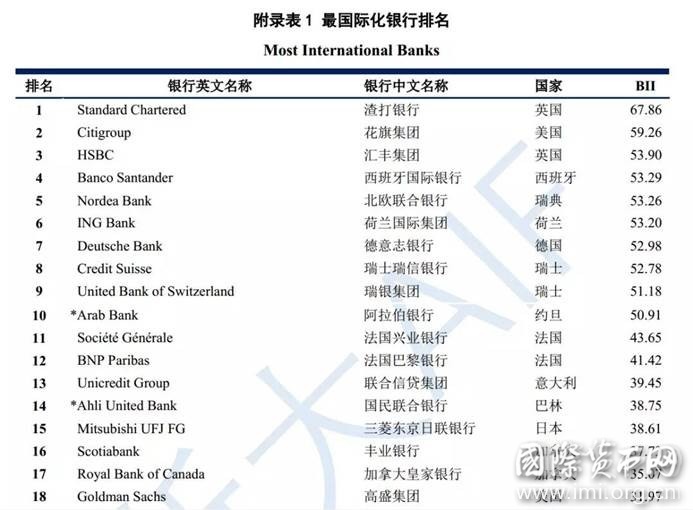
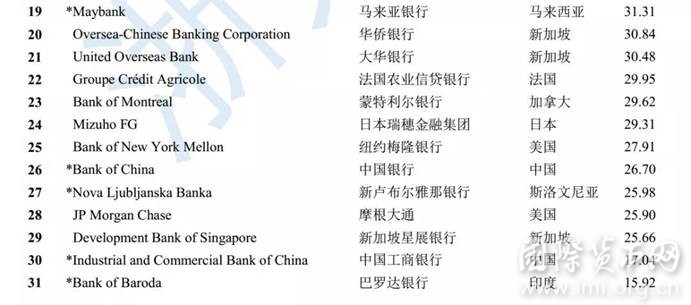
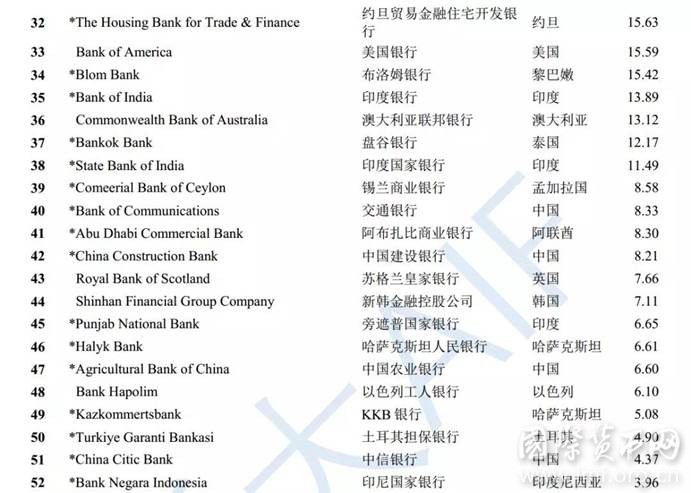
2017年,我们选择境外数据较为全面的64家银行(资产总额约53万亿美元,相当于全球GDP的65%)进行BII排名,展现各个银行的国际化水平。
一、 最国际化银行
2017年,我们选择境外数据较为全面的64家银行(资产总额约53万亿美元,相当于全球GDP的65%)进行BII排名,展现各个银行的国际化水平。
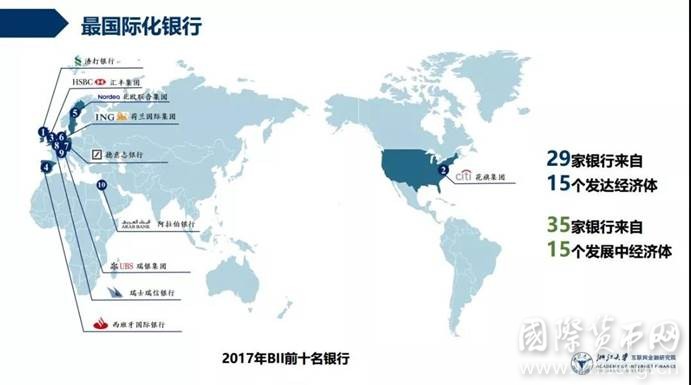 2017年,我们选择境外数据较为全面的64家银行(资产总额约53万亿美元,相当于全球GDP的65%)进行BII排名,展现各个银行的国际化水平。
2017年,我们选择境外数据较为全面的64家银行(资产总额约53万亿美元,相当于全球GDP的65%)进行BII排名,展现各个银行的国际化水平。
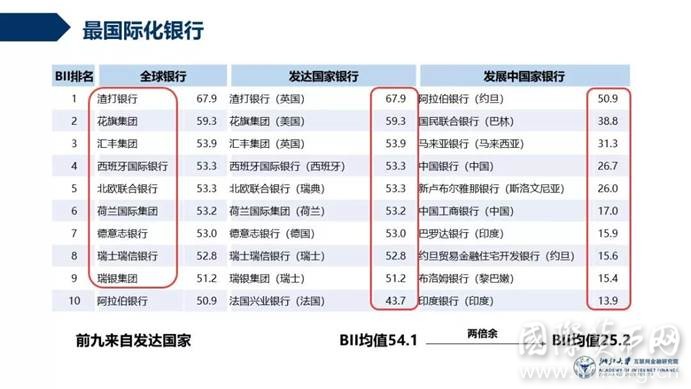 注:完整排名见“附录表1”。花旗集团2017年数据有缺失,但其前几年数据较全,本表对其BII值进行了合理预测。
注:完整排名见“附录表1”。花旗集团2017年数据有缺失,但其前几年数据较全,本表对其BII值进行了合理预测。
- 最国际化的银行基本来源于发达国家。2017年,全球银行BII前十名中9家来自发达国家。BII以银行境外经营数据占比衡量银行国际化水平,是为“最国际化银行”,其排名表现反映出,当前国际舞台上的跨国银行,仍以国际化历史更为久远的发达国家银行为主。
- 发达国家银行国际化水平总体较高。排名前十的发达国家银行BII数值基本超过50分,境外发展与境内同等重要甚至超越境内发展。欧洲地区银行因国内市场规模较小、区域地缘关系密切,国际化水平普遍较高,在发达国家银行前十名中占据9席。
- 发展中国家银行国际化水平参差不齐。一方面,发展中国家前十名,仅阿拉伯银行BII数值达50分以上,仅有5家银行BII数值超过20分,整体水平较低,且各银行间差距较大。另一方面,前十名中,约旦、中国、印度各有两家银行,地缘关系、宗教文化、国内经济发展均对银行国际化有较大影响。
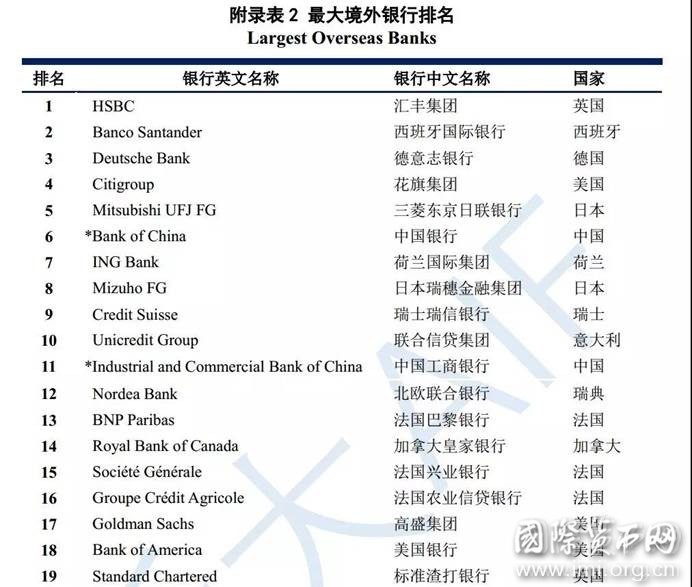
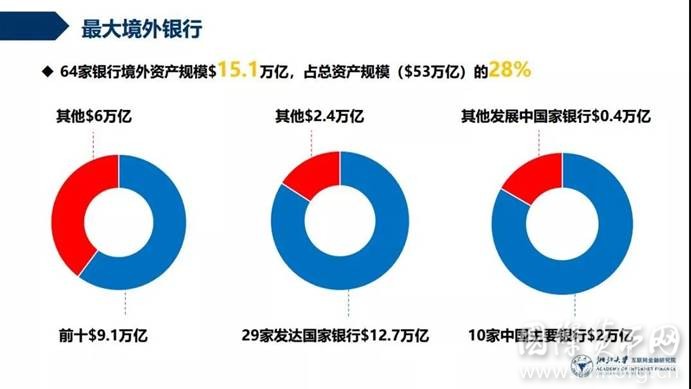 报告以银行境外资产代表各行境外银行规模,得“最大境外银行”排名。
报告以银行境外资产代表各行境外银行规模,得“最大境外银行”排名。
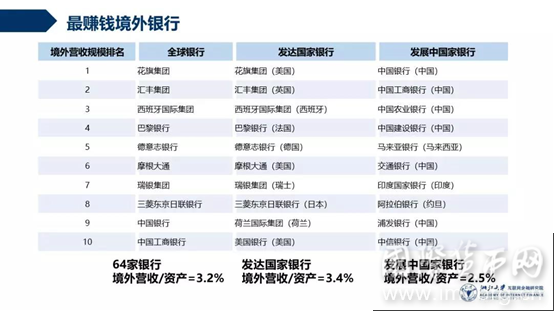 表2 2017年最大境外银行排名(前十)
注:完整排名见“附录表2”。所有银行境外资产数据以该行资产负债表日汇率换算为美元,之后进行境外资产规模排名。花旗集团2017年数据有缺失,但其前几年数据较全,本表对其境外资产规模进行了合理预测。
全球银行境外资产规模庞大。参与2017年BII评分的64家银行,其境外资产总规模约15.1万亿美元,超2017年中国GDP总量(约12.2万亿美元,该数据来源于世界银行数据库),其中前十名银行境外总资产达9.1万亿美元,占所有银行境外资产总量的一半以上。
发达国家银行境外资产规模远超发展中国家。境外资产规模前十名中9家来自发达国家,且29家发达国家银行境外资产总规模约为12.7万亿美元,占全球境外银行规模的84%,是35家发展中国家银行境外资产总规模(2.4万亿美元)的五倍以上。发达国家银行中,欧美地区银行境外资产规模较大,日本代表银行表现也较为突出。
中国成为银行境外资产规模最大的发展中国家。截至2017年底,中国主要银行境外资产规模逾2万亿美元,超意大利当年的GDP总量。中国银行作为唯一进入全球银行境外资产排名前十的发展中国家银行,位列第6名,中国成为唯一在“最大境外银行”前十名中获得一席之地的发展中国家,且在发展中国家银行前十名中占据7席。
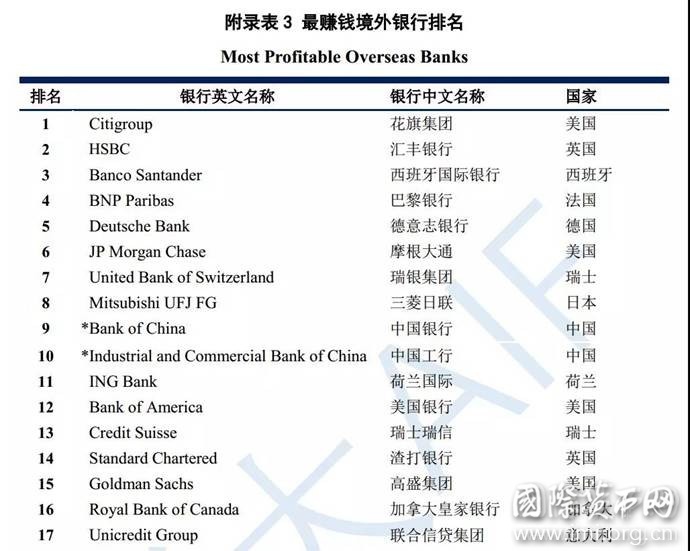
三、 最赚钱境外银行
表2 2017年最大境外银行排名(前十)
注:完整排名见“附录表2”。所有银行境外资产数据以该行资产负债表日汇率换算为美元,之后进行境外资产规模排名。花旗集团2017年数据有缺失,但其前几年数据较全,本表对其境外资产规模进行了合理预测。
全球银行境外资产规模庞大。参与2017年BII评分的64家银行,其境外资产总规模约15.1万亿美元,超2017年中国GDP总量(约12.2万亿美元,该数据来源于世界银行数据库),其中前十名银行境外总资产达9.1万亿美元,占所有银行境外资产总量的一半以上。
发达国家银行境外资产规模远超发展中国家。境外资产规模前十名中9家来自发达国家,且29家发达国家银行境外资产总规模约为12.7万亿美元,占全球境外银行规模的84%,是35家发展中国家银行境外资产总规模(2.4万亿美元)的五倍以上。发达国家银行中,欧美地区银行境外资产规模较大,日本代表银行表现也较为突出。
中国成为银行境外资产规模最大的发展中国家。截至2017年底,中国主要银行境外资产规模逾2万亿美元,超意大利当年的GDP总量。中国银行作为唯一进入全球银行境外资产排名前十的发展中国家银行,位列第6名,中国成为唯一在“最大境外银行”前十名中获得一席之地的发展中国家,且在发展中国家银行前十名中占据7席。
三、 最赚钱境外银行
 本期报告以银行境外营收规模代表各行境外经营成果,得“最赚钱境外银行”排名。
本期报告以银行境外营收规模代表各行境外经营成果,得“最赚钱境外银行”排名。
 表3 2017年最赚钱境外银行排名(前十)
注:完整排名见“附录表3”。所有银行境外营收数据以该行资产负债表日汇率换算为美元,之后进行境外营收规模排名。
全球银行境外经营成果显著。64家银行境外营收总规模约4900亿美元,是所有银行营业收入总额的30.8%,其中前十名银行境外总营收达3000亿美元,超过其余54家银行境外营收总额。
发达国家银行境外经营更胜发展中国家银行。境外营收规模前十名中8家来自发达国家,且29家发达国家银行境外营收总规模接近4300亿美元,占全球银行境外营收规模的87.8%,是35家发展中国家银行境外营收总规模(600亿美元)的七倍以上。且发达国家境外营收约占其境外资产的3.4%,高于发展中国家银行境外资产收入率(2.5%),境外经营能力更高。
发展中国家银行境外发展以金砖国家银行为最高水平。35家发展中国家银行中,15家金砖国家银行境外营收总规模约530亿美元,占据35家发展中国家银行境外营收总规模的近88%,引领发展中国家银行国际发展。金砖国家作为新兴经济体的突出代表,国际影响力日盛,金融机构的国际活跃度也在愈益增强。
四、 国际化的不同选择
表3 2017年最赚钱境外银行排名(前十)
注:完整排名见“附录表3”。所有银行境外营收数据以该行资产负债表日汇率换算为美元,之后进行境外营收规模排名。
全球银行境外经营成果显著。64家银行境外营收总规模约4900亿美元,是所有银行营业收入总额的30.8%,其中前十名银行境外总营收达3000亿美元,超过其余54家银行境外营收总额。
发达国家银行境外经营更胜发展中国家银行。境外营收规模前十名中8家来自发达国家,且29家发达国家银行境外营收总规模接近4300亿美元,占全球银行境外营收规模的87.8%,是35家发展中国家银行境外营收总规模(600亿美元)的七倍以上。且发达国家境外营收约占其境外资产的3.4%,高于发展中国家银行境外资产收入率(2.5%),境外经营能力更高。
发展中国家银行境外发展以金砖国家银行为最高水平。35家发展中国家银行中,15家金砖国家银行境外营收总规模约530亿美元,占据35家发展中国家银行境外营收总规模的近88%,引领发展中国家银行国际发展。金砖国家作为新兴经济体的突出代表,国际影响力日盛,金融机构的国际活跃度也在愈益增强。
四、 国际化的不同选择
 我们利用106家银行近十年的BII数值对全球银行业的国际化发展情况进行描述,其中,发达国家银行42家,来自15个国家,发展中国家银行64家,来自23个国家。
我们利用106家银行近十年的BII数值对全球银行业的国际化发展情况进行描述,其中,发达国家银行42家,来自15个国家,发展中国家银行64家,来自23个国家。
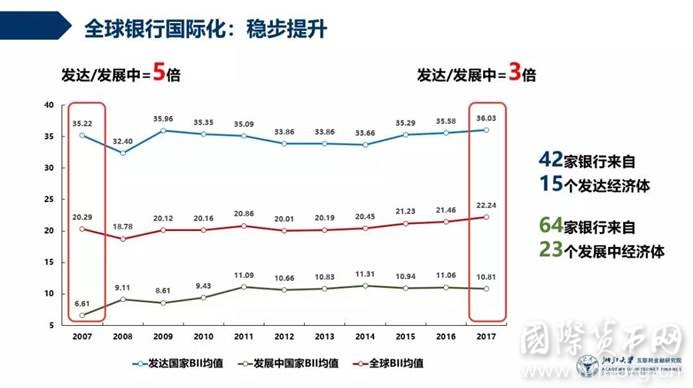 图1 2007~2017年全球银行BII均值变动
注:本图以106家银行为基础样本,部分银行BII在个别年份为缺省值。
全球银行业国际化水平近十年波动较小,自2012年后国际化水平总体呈上升态势。一方面,近年来经济增速回升,主要经济体稳步发展、全球贸易和投资回暖、金融市场预期向好、内外部环境改善,成为银行积极进行境外扩张的动力和前提;另一方面,尽管保护主义对发展的威胁不减,但区域间的密切交往仍在进行,无论是环太平洋区的经贸往来,还是欧洲联盟以及“一带一路”沿线国家间的频繁合作,均为各国企业及金融机构的境外发展提供了重要机遇。
约三成系统重要性银行国际化水平下降,众多原因促使部分银行转变国际化扩张战略。一是经济环境使然,逆全球化和贸易保护主义抬头,地缘政治冲突多点爆发,风险因素和不确定性的加速积累使银行更具谨慎意识。二是金融监管趋严,自2015年起,金融稳定理事会通过《总损失吸收能力原则及条款》,提高系统重要性银行的合规难度,以有效维护增长。三是发展战略出现变化,更多银行关注重点开始由“量”转“质”,相较规模扩张更注重资产配置的优化和布局结构的改善。
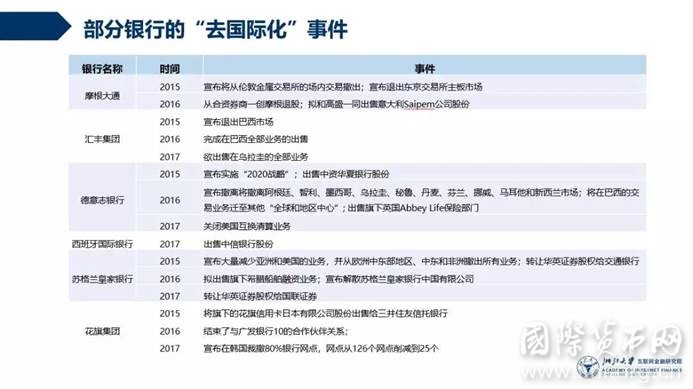
表4 部分银行的“去国际化”事件
图1 2007~2017年全球银行BII均值变动
注:本图以106家银行为基础样本,部分银行BII在个别年份为缺省值。
全球银行业国际化水平近十年波动较小,自2012年后国际化水平总体呈上升态势。一方面,近年来经济增速回升,主要经济体稳步发展、全球贸易和投资回暖、金融市场预期向好、内外部环境改善,成为银行积极进行境外扩张的动力和前提;另一方面,尽管保护主义对发展的威胁不减,但区域间的密切交往仍在进行,无论是环太平洋区的经贸往来,还是欧洲联盟以及“一带一路”沿线国家间的频繁合作,均为各国企业及金融机构的境外发展提供了重要机遇。
约三成系统重要性银行国际化水平下降,众多原因促使部分银行转变国际化扩张战略。一是经济环境使然,逆全球化和贸易保护主义抬头,地缘政治冲突多点爆发,风险因素和不确定性的加速积累使银行更具谨慎意识。二是金融监管趋严,自2015年起,金融稳定理事会通过《总损失吸收能力原则及条款》,提高系统重要性银行的合规难度,以有效维护增长。三是发展战略出现变化,更多银行关注重点开始由“量”转“质”,相较规模扩张更注重资产配置的优化和布局结构的改善。
表4 部分银行的“去国际化”事件
 总而言之,过去一年,全球经济形势依然复杂,全球银行业的国际化发展方兴未艾,有银行积极迈出国际步伐,亦有银行谨慎调整全球战略,形成了层次多样的国际化格局。未来,在国际经济与政治尚不明朗的环境下,银行应审慎制定国际化战略,做到“走出去”与跨境风险防范并举,并善于利用各类区域合作机遇提升国际化水平。
The English Version:
2018 Bank Internationalization Report
In the past year, the global economy has continued to recover and total demand has rebounded, but economic downside risks remain. In the meanwhile, the shift in monetary policy, the deterioration of the debt backlog, and the anti-globalization trend have become hidden dangers of economic growth. In an environment where opportunities and challenges coexist, how do banks in various countries devote themselves to international development and how the level of internationalization of global banks change? “The Internationalization of Global Banks” series of reports continue to focus on the bank's overseas assets, revenue, and branch performance, demonstrating the internationalization of major banks around the world by the Bank Internationalization Index (BII). As the fourth phase of the series of reports, 2018 Bank Internationalization Report selects 106 banks from 38 major economies for in-depth analysis. The total assets of these banks in 2017 were about 70 trillion US dollars, accounting for 86% of the global GDP of the year. From developed countries to developing countries, from Europe, America, to Asia and Africa, they include major banks in major economies, and represent the status quo of the global-banking-industry internationalization.
I Most International Banks
In 2017, we selected 64 banks with a relatively comprehensive overseas data (total assets of approximately $53 trillion, about 65% of global GDP) to conduct BII rankings, which shows the internationalization level of each bank.
总而言之,过去一年,全球经济形势依然复杂,全球银行业的国际化发展方兴未艾,有银行积极迈出国际步伐,亦有银行谨慎调整全球战略,形成了层次多样的国际化格局。未来,在国际经济与政治尚不明朗的环境下,银行应审慎制定国际化战略,做到“走出去”与跨境风险防范并举,并善于利用各类区域合作机遇提升国际化水平。
The English Version:
2018 Bank Internationalization Report
In the past year, the global economy has continued to recover and total demand has rebounded, but economic downside risks remain. In the meanwhile, the shift in monetary policy, the deterioration of the debt backlog, and the anti-globalization trend have become hidden dangers of economic growth. In an environment where opportunities and challenges coexist, how do banks in various countries devote themselves to international development and how the level of internationalization of global banks change? “The Internationalization of Global Banks” series of reports continue to focus on the bank's overseas assets, revenue, and branch performance, demonstrating the internationalization of major banks around the world by the Bank Internationalization Index (BII). As the fourth phase of the series of reports, 2018 Bank Internationalization Report selects 106 banks from 38 major economies for in-depth analysis. The total assets of these banks in 2017 were about 70 trillion US dollars, accounting for 86% of the global GDP of the year. From developed countries to developing countries, from Europe, America, to Asia and Africa, they include major banks in major economies, and represent the status quo of the global-banking-industry internationalization.
I Most International Banks
In 2017, we selected 64 banks with a relatively comprehensive overseas data (total assets of approximately $53 trillion, about 65% of global GDP) to conduct BII rankings, which shows the internationalization level of each bank.
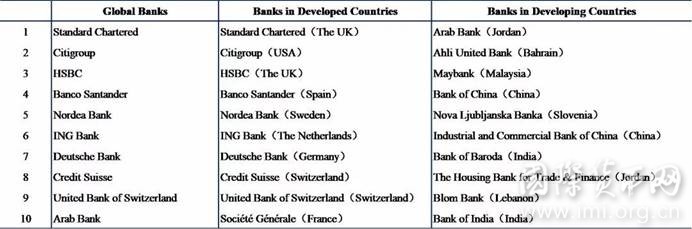 Table 1 Most International Banks in 2017 (Top 10)
Note: Citigroup's data of 2017 is missing, but its previous years' data is relatively complete. In this table, a reasonable prediction of its BII value is made.
Table 1 Most International Banks in 2017 (Top 10)
Note: Citigroup's data of 2017 is missing, but its previous years' data is relatively complete. In this table, a reasonable prediction of its BII value is made.
- The most international banks are mostly from developed countries. In 2017, 9 of the top 10 global bank BIIs were from developed countries. BII measures the internationalization level of banks based on the proportion of overseas business data of banks, which is the “most internationalized bank”, and the ranking performance reflects that the current multinational banks on the international stage are still dominated by developed countries with more internationalized history.
- The level of internationalization of banks in developed countries is generally high.The BII value of the top ten developed countries' banks is basically more than 50 points. The overseas development is as important as the domestic territory and even surpasses the domestic development. Due to the small size of the domestic market and the close geographical relationship, the European regional banks generally have a high level of internationalization, occupying nine seats in the top ten banks in developed countries.
- The level of internationalization of banks in developing countries is uneven.On the one hand, among the top ten in developing countries, only the Arab Bank BII reaches the value of 50 points, and only five banks BII value exceeds 20 points, which show that the overall level is low and the gap between banks is large. On the other hand, among the top ten, Jordan, China, and India each have two banks. Geopolitical relations, religious culture, and domestic economic development all have a great impact on the internationalization of banks.
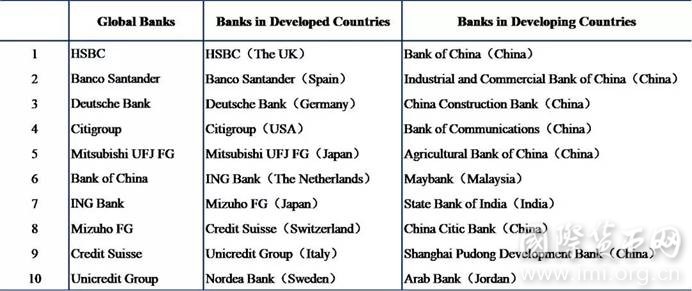 Table 2 Largest Overseas Banks in 2017(Top 10)
Note: All bank overseas asset data is converted into US dollars at the exchange rate of the bank's balance sheet date, and then the offshore asset scale is ranked. Citigroup's data in 2017 is missing, but its data in previous years is relatively complete. In this table, a reasonable forecast for the scale of its overseas assets is made.
Table 2 Largest Overseas Banks in 2017(Top 10)
Note: All bank overseas asset data is converted into US dollars at the exchange rate of the bank's balance sheet date, and then the offshore asset scale is ranked. Citigroup's data in 2017 is missing, but its data in previous years is relatively complete. In this table, a reasonable forecast for the scale of its overseas assets is made.
- The scale of overseas bank assets is huge.The total size of the 64 banks overseas assets is about $15.1 trillion, exceeding the total GDP of China in 2017 (about $12.2 trillion). The top ten banks’ total overseas assets reached $9.1 trillion, accounting for more than half of the total overseas assets of all banks.
- The scale of overseas assets of developed countries' banks far exceeds that of developing countries. Among the top ten overseas assets, nine of them are from developed countries, and the total assets of 29 developed countries’ banks are about $12.7 trillion, which accounts for 84% of the world’s overseas banks, and is more than five times the scale of the total assets of 35 developing countries’ banks ($2.4 trillion). Among the banks in developed countries, the scale of overseas assets of banks in Europe and the United States is relatively large, and the performance of Japanese banks is prominent as well.
- China has become the developing country with the largest overseas assets of banks.As of the end of 2017, the scale of overseas assets of major banks in China exceeded US$2 trillion, exceeding the total GDP of Italy in that year. Bank of China, ranked as the only developing country bank to enter the top 10 of the global overseas banks, ranking sixth, and China became the only developing country to gain a place in the top ten of the “largest overseas banks” and it takes 7 seats out of the top 10 banks from developing countries.
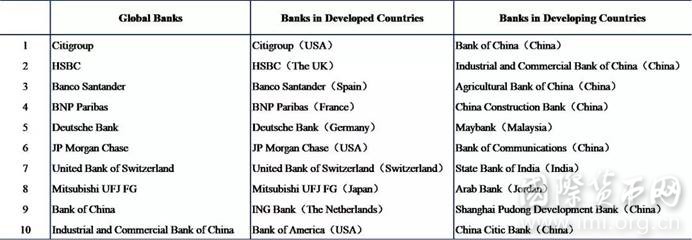 Table 3 Most Profitable Overseas Banks in 2017(Top 10)
Note: All bank external revenue data is converted into US dollars at the exchange rate of the bank's balance sheet date, and then the overseas revenue scale is ranked.
Table 3 Most Profitable Overseas Banks in 2017(Top 10)
Note: All bank external revenue data is converted into US dollars at the exchange rate of the bank's balance sheet date, and then the overseas revenue scale is ranked.
- The global bank's overseas operations have achieved remarkable results. The total overseas revenue of 64 banks is about $490 billion, which is approximately equal to 30.8% of the total operating income of all banks. The top 10 banks have total overseas revenues of $300 billion, which exceeds the total overseas revenue of the remaining 54 banks.
- The overseas operations of banks in developed countries are better than those in developing countries.Among the top 10 overseas revenues, 8 are from developed countries, and the total overseas revenues of 29 banks from developed countries are close to $430 billion, accounting for 87.8% of the total overseas revenues. It is more than seven times the size of the overseas bank revenues of 35 developing countries ($60 billion). Moreover, the overseas revenues of developed countries accounts for 3.4% of its overseas assets, which is higher than the overseas assets income rate of developing countries (2.5%), and the overseas business capacity is higher.
- The BRICS Banks represent the highest level of the overseas development of banks.Among the 35 banks from developing countries, 15 are from BRICS. And their overseas revenue is close to $53 billion, accounting for 88% of the total overseas bank revenue of 35 banks, leading the international development of banks in developing countries. As a prominent representative of emerging economies, the BRICS is increasingly influential around the world, and the international activity of financial institutions is increasing as well.
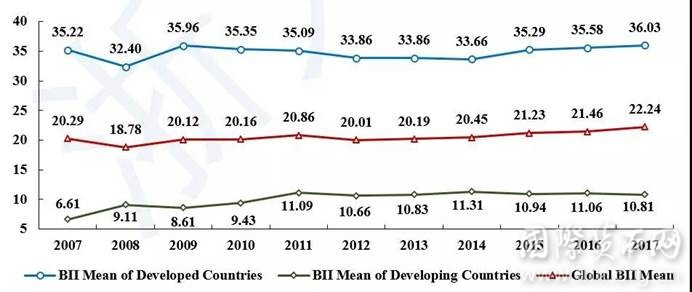 Note: This chart is based on 106 banks, and some banks BII are default values in individual years.
Figure 1 Global Bank BII Mean Fluctuation from 2007 to 2017
Note: This chart is based on 106 banks, and some banks BII are default values in individual years.
Figure 1 Global Bank BII Mean Fluctuation from 2007 to 2017
- The internationalization level of the global banking industry has been less volatile in the past decade, and since 2012, the internationalization level has generally increased.On the one hand, the economic growth rate has rebounded in recent years, and the steady development of major economies, the recovery of global trade and investment, the expected improvement of financial markets, and the improvement of internal and external environment have become the driving force and premise for banks to expand overseas actively. On the other hand, although protectionism’s threat to development is not diminished, close exchanges between regions are still going on, such as economic and trade exchanges in the Pacific Rim and frequent cooperation between the European Union and countries along the Belt and Road. They all provide important opportunities for the overseas development of enterprises and financial institutions in various countries.
- About 30% of systemically important banks have declined in internationalization, and many reasons have prompted some banks to transform their international expansion strategies.First, banks are more cautious because of the risen counter-globalization and trade protectionism, the exploded geopolitical conflicts, and the accelerated accumulation of risk factors and uncertainties. Second, financial supervision has become stricter. Since 2015, the Financial Stability Board has adopted the Principles and Clauses for Total Loss Absorptive Capacity to improve the compliance difficulty of systemically important banks to maintain growth effectively. Third, the development strategy has changed. More banks have begun to focus on “quality” from “quantity”. Compared with scale expansion, they have paid more attention to the optimization of asset allocation and the improvement of layout structure.






分享到:
扩展阅读
专家工作室EXPERTS
热门视点VIEWS
文章标签TAGS
